E-Business vs E-Commerce: Understand the Difference
It is common to think that e-business and e-commerce are synonymous, so it is important to differentiate between them. In today’s dynamic business landscape, you can take advantage of trends by learning the difference between E-Business vs E-Commerce and setting up a successful e-commerce business.
A subset of e-business is e-commerce, which includes all digital elements of running a business online. E-business encompasses all digital components of an organization.
Our goal in this article is to help you better understand how e-commerce differs from e-business and how you can use that knowledge to grow your company.
E-Commerce in 2024: Growth Projections and Beyond Traditional Transactions
With the e-commerce market expected to grow 10.5% or $1.2 trillion in 2024 after its phenomenal growth in 2020, it is now expected to stabilize to pre-pandemic levels. E-commerce commerce is predicted to be the world’s largest market in China, among other countries, where the same scenario holds true.
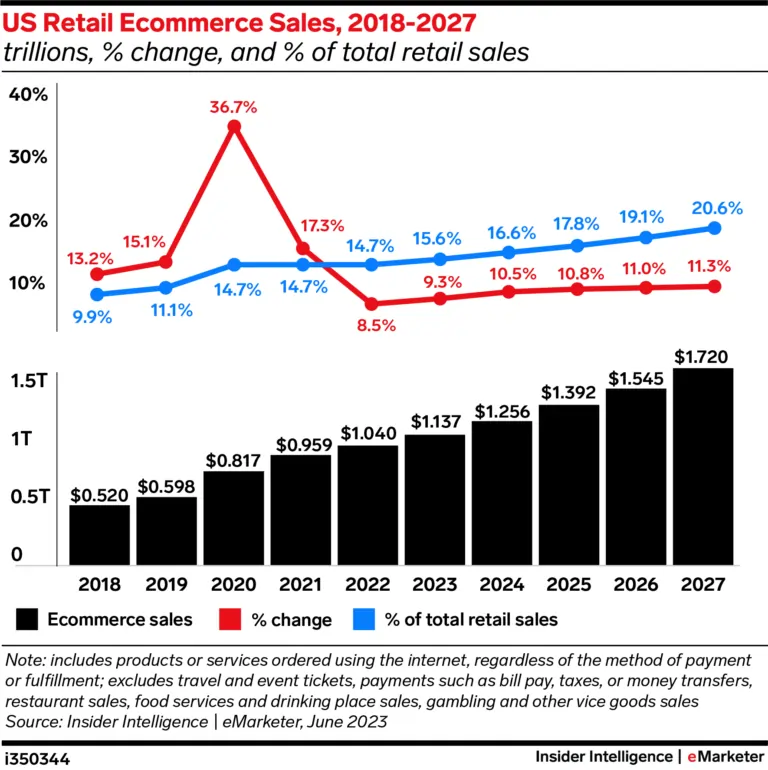
E-commerce is the exchange of goods and services electronically, such as buying clothes online with a credit card from an online store.
E-commerce transactions need to be completed and paid online to be considered an e-commerce transaction. Purchasing pizza through an app and paying for it in cash upon delivery cannot be considered an e-commerce transaction.
Online payment methods, online customer service, and online accounting software are other examples of e-commerce activities.
C2C (consumer-to-consumer) and C2B (consumer-to-business) are consumer-to-consumer transactions; while B2A (business-to-administration) and C2A (consumer-to-administration) are business-to-administration transactions.
B2B E-Commerce
Usually, large-scale wholesale transactions occur between two business entities via electronic means.
B2C E-Commerce
It is the largest and most common form of eCommerce, including giant platforms such as Amazon, where companies sell directly to the end user.
C2C E-Commerce
Platforms like Facebook Marketplace enable individual sellers to sell direct to other individuals. This includes selling preloved items and starting a micro business online.
C2B E-Commerce
It can also be individual consumers who are paid by a company to market the products of a company, which are provided by independent consultants or freelancers.
B2A E-Commerce
As part of its compliance with regulatory requirements like social security, permits, and others, a business entity might make a deal with a government regulator. This is what is known as a B2G (business to government) transaction.
C2A E-Commerce
It is now possible to transact completely electronically with a government entity. This includes the application process and payment of legal documents like a birth certificate, as well as paying taxes and fines.
A new type of “online” or “digital” commerce has emerged in recent years, namely social commerce and mobile commerce, both technically not considered “e-commerce”.
As differs from social commerce, e-commerce consists of online shopping via dedicated apps or online stores, like TikTok, Facebook, and Instagram.

Using mobile wallets and contactless payments, m-commerce allows for a wide range of payments. Since it involves specifically purchasing and paying for goods and services using a mobile device, m-commerce is considered a subcategory of e-commerce. E-commerce primarily utilizes credit cards and other traditional payment methods.
The Broad Scope of E-Business: Moving Past E-Commerce to Efficient Workflows
The concept of e-business encompasses a much broader scope than just e-commerce. It describes integrating electronic technology into every aspect of a business’ operation. It encompasses transactions done online, as well as various other electronic interactions that make a business more efficient.
A lot of other aspects of e-business are included, including customer relationship management, supply chain management, customer education, email marketing, monetary transactions, and setting up online stores.
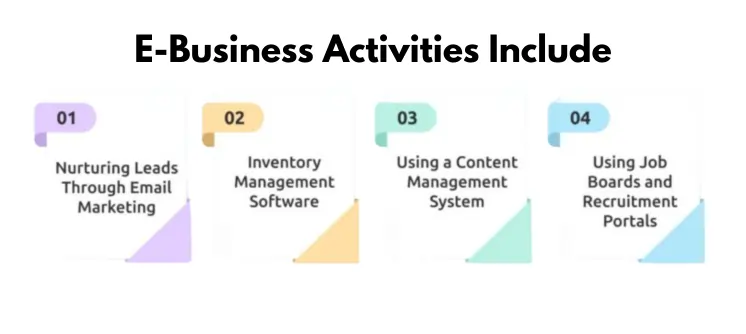
Among the activities associated with e-business are:
- Email marketing for lead nurturing and client relationship building
- Automated alerts can be used for low stock activities when tracking inventory using inventory management software
- Content development, editing, and publishing workflows are managed by a content management system
- Employers can manage job applications and collect employee data on job boards and recruitment portals
You can transform your business to an e-business by digitizing the above business functions, if you do not have an electronic system.
In addition, e-business solutions help companies personalize marketing strategies to enhance customer engagement and loyalty, resulting in greater efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced customer experiences.
A business that uses e-commerce can be classified into two types:
Pure Play
There are a number of examples of this type of e-business, from SaaS businesses to websites that provide comparisons and reviews of services, such as hotels, flights, etc.
Brick-and-click
Generally, e-businesses can operate online and offline. For example, clothing companies could have physical stores where customers browse and try on different styles, as well as online stores where customers can make purchases whenever they want.
Understanding E-Commerce and E-Business: A Side-by-Side Comparison
Despite their similarities, e-commerce and e-business differ in their scope and focus. It’s common for business people to mix them up.
As a result of e-commerce, businesses set up online stores, display products and services, and let customers pay online. It is primarily concerned with online transactions. Consumers and businesses alike enjoy the benefits of shopping and selling online. The transactional nature of e-commerce is central to its definition. Popular e-commerce platforms like Amazon, eBay, and Shopify have revolutionized e-commerce.
In contrast, e-business incorporates not only buying and selling elements, but also integrating electronic technology into a wide variety of internal and external business processes. As a result of e-business, suppliers, partners, and customers can interact electronically, improving operational efficiency and strategic decisions.
E-commerce is a component of any e-business, but it is not required to have an e-business. In the marketing industry, for example, email marketing is used to nurture leads and content management systems are used to produce and distribute content. It does not, however, engage in online sales or buying and selling.
Nevertheless, e-commerce stores will need many online electronic systems in order to prosper and scale their operations, such as inventory tracking software, warehouse management software, and accounting software, among others.
Key Differences Between E-Commerce and E-Business
| E-commerce | E-business |
| Only involves online commercial transactions | Involves any business activity done electronically |
| Narrow concept – a subset of e-business | Broad concept – the superset of e-commerce |
| Transactions mainly use one website or app | Uses multiple websites, ERPs, CRMs, etc., to connect business processes |
| Relies on the internet | Can use the internet, intranet, or extranet |
| Involves external business processes | Involves external and internal business processes |
| Widely used in the B2C context | Mostly appropriate in the B2B context |
There are several areas where e-commerce and e-business differ significantly, despite both having a digital foundation.
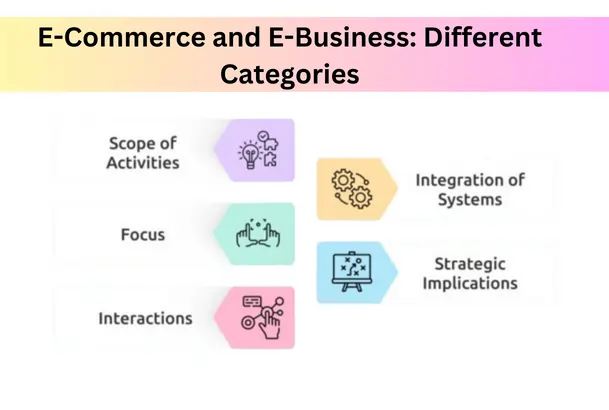
Scope of Activities
The e-commerce industry is primarily concerned with electronic commerce transactions. In addition to providing customers with a convenient and seamless shopping experience, it also provides the ability to purchase products and services digitally. In spite of its ability to be used anywhere, it’s most prevalent in B2C (business-to-consumer) contexts.
On the other hand, e-business involves the integration of electronic technology into every aspect of business. E-business operations are not always commercial in nature and e-commerce only represents a small part. They are most often appropriate for B2B businesses.
Focus
Creating an efficient and user-friendly e-commerce platform is imperative for attracting customers online. User-friendly website design, intuitive navigation, secure payment gateways, and efficient checkout processes all play a key role.
Despite the importance of customer experience in e-business, its scope extends farther than just transactions. It aims to improve overall business processes, operational efficiency, and communication, which in turn help to improve customer experience.
Interactions
As the name implies, e-commerce interactions are primarily transactional, involving the exchange of goods and services for money. A web-based website or app is used to conduct these interactions, and they always involve the internet. The interactions are usually short-term and revolve around selecting products, paying, and delivering them. As the transaction is external, the other party is usually located in another location, so an internet connection is required.
The interaction between suppliers, distributors, partners, and customers in e-business, on the other hand, is more diverse. The e-business ecosystem enables various entities to communicate, share data, and collaborate with one another. A number of websites and business systems will be used to complete these interactions, whether they are carried out internally or externally. Using an intranet or extranet is not always required for completing a transaction; it is possible to do it through an intranet or extranet as well.
Integration of Systems
These systems can often be standalone or integrated with internal processes for setting up online storefronts, managing product listings, and accommodating secure online transactions.
Integration of systems is more important in e-business. Through the use of shared software solutions, a company’s departments and functions can exchange data in real-time, collaborate efficiently, and make better decisions.
Strategic Implications
A successful e-commerce strategy will increase conversion rates, average order value, and website traffic by marketing products online and optimizing conversion rates.
In contrast, e-business strategies aim to improve efficiency, improve customer relationships, and drive long-term growth for businesses by aligning technology with overall business objectives.
Choosing Between E-Commerce and E-Business: Aligning with Your Strategic Goals
The main issue is not whether to use e-commerce or e-business, nor if one is better than the other. Each has its own set of specific and unique concerns.
A business’s strategic goals and the nature of its business determine whether or not to focus on e-business or e-commerce.
To enhance the customer shopping experience, businesses that sell primarily online should invest in a robust e-commerce platform that allows them to create user-friendly online stores, optimize product listings, and provide secure payment gateways.
An e-business approach is, on the other hand, recommended for businesses wishing to transform their operations and interactions through technology. Various processes, including procurement, inventory management, customer service, and marketing, must be streamlined through the implementation of integrated software solutions.
To become a modern organization that thrives in today’s digital era, most organizations need a robust e-commerce platform and a digital transformation of their existing processes.
Importance of Understanding the Distinction
It is necessary for business owners and decision-makers to have a clear understanding of the differences between ecommerce and e-business if they want to succeed in the digital environment.
In embracing a holistic e-business approach, you can strengthen relationships with partners and improve customer experiences by integrating e-business into all of your internal processes.
You can also tailor strategies to address the dynamic demands of online consumers by comprehending the potential and scope of e-commerce to identify new growth avenues.
Final Thoughts
It is understood that e-commerce and e-business are related concepts, but their scope, focus, and implications are significantly different. E-commerce deals mainly with online transactions, whereas e-business involves a wide range of electronic interactions within and beyond the world of commerce.
To determine whether e-commerce is the best option for streamlined online sales or e-business strategies are the best option for comprehensive digital transformation, businesses need to evaluate their goals and operational needs. An organization’s success may be greatly influenced by the choice between these approaches.
E-business and e-commerce have significant differences. You must understand these differences in order to be prepared to adapt, innovate, and seize opportunities that will ultimately shape the success of your business.
People Also Ask
What is the difference between e-commerce and e-business?
E-commerce refers specifically to the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet. It involves online transactions, such as purchasing products from an online store.
E-business, on the other hand, is a broader term that encompasses all aspects of running a business using the internet. This includes not only buying and selling but also activities like online marketing, customer service, and electronic transactions between businesses.
What is the difference between business and commerce?
Business refers to the broader concept of any organization or entity engaged in commercial, industrial, or professional activities. It includes activities related to production, distribution, and sale of goods and services.
Commerce, on the other hand, specifically refers to the exchange of goods and services, typically involving transactions between businesses or between businesses and consumers.
What is the difference between e-business and M-commerce?
E-business involves conducting business processes over the internet. It includes activities such as online shopping, electronic payments, online marketing, and customer service.
M-commerce, or mobile commerce, refers to conducting business transactions using mobile devices such as smartphones or tablets. It involves activities like mobile banking, mobile shopping, and mobile ticketing.
What do you understand about e-commerce?
E-commerce, short for electronic commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet or other electronic networks. It involves online transactions conducted between businesses and consumers (B2C), between businesses (B2B), or between consumers (C2C). E-commerce encompasses various activities such as online retailing, online auctions, electronic payments, and online marketplaces.







